Most men have dealt with their fair share of testicular pain. Whether it resulted from an accidental sporting blow or getting trapped in a zipper, testicular pain is a common male health issue that knows no bounds. It can affect men of all ages, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, crippling pain.
And testicle pain doesn’t discriminate – it can affect one or both testicles and is usually caused by injury or infection. However, it can also be caused by several other conditions, including inflammation, trauma, testicular torsion or even testicular cancer. So, if it isn’t as apparent as a sporting incident or wardrobe malfunction, there’s a chance it may be the result of one of the following causes of testicular pain.
What does testicular pain feel like?
Testicular pain can feel differently from man to man, but some common symptoms include:
- Aching or throbbing pain: This can be a dull or sharp pain that is felt in one or both testicles.
- Soreness or tenderness: You may experience tenderness or soreness in your testicles when you touch them or when you wear tight clothing.
- Swelling or lumps: You may notice swelling or lumps in one or both testicles.
- Discomfort or tightness: Some people describe the discomfort or tightness as a sharp, stabbing sensation or as a feeling of fullness or pressure in the testicles.
- Bruising or redness: In some cases, you may also notice bruising or redness in the area.
It’s important to note that the symptoms and severity of testicular pain can vary greatly, so if you’re experiencing discomfort, it’s best to speak to your doctor to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Potential causes of testicular pain
1. Sexual activity
One of the most common causes of testicular pain is sex. During sexual activity, the testicles can be bumped, squashed, or pulled, which can cause pain and discomfort. To prevent testicular pain during sexual activity, use proper lubrication, ask your partner to go easy down there, and avoid rough or vigorous pulling and tugging on the testicles.
If you experience testicular pain after sex, it is important to talk to your doctor about it. If left ignored, the risk of developing performance anxiety and associated erectile dysfunction could increase.
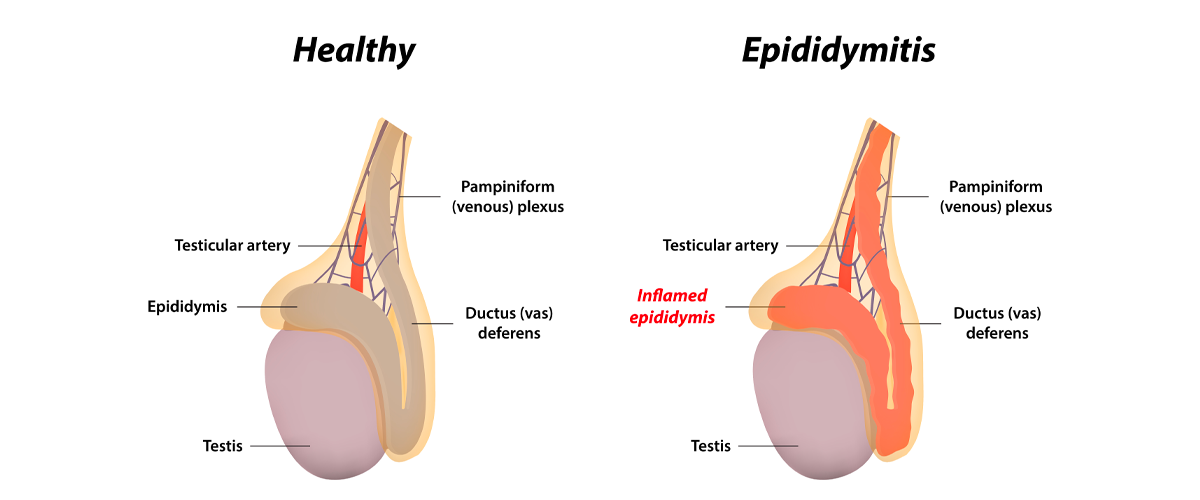
2. Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a condition that affects the epididymis, a small organ located behind the testicles (learn more about male anatomy). In men, the epididymis transports sperm from the testicles. When epididymitis occurs, the epididymis becomes inflamed and swollen, causing pain in the testicles and scrotum. Symptoms of epididymitis may include a swollen testicle, pain or tenderness in the scrotum or testicle, pain when urinating or ejaculating, and fever.
Bacterial infections cause most cases of epididymitis. However, it can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or an autoimmune disorder. Treatment for epididymitis typically involves antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. In some cases, surgery may also be necessary to relieve pain and inflammation.
3. Hernias
A hernia is when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weakened or abnormal area of the abdominal wall. Although hernias can occur anywhere in the abdominal cavity, they are most commonly found in the area of the groin and can affect the testicles.
When a hernia affects the testicles, it can cause severe pain and discomfort. Hernias can cause the testicles to press against the weakened abdominal wall, creating pressure and inflammation. In some cases, this pressure can be so intense that it causes the blood vessels in the testicles to become blocked, leading to a condition known as testicular torsion.
In addition to pain, hernias can cause swelling and tenderness in the testicular area. Other hernia symptoms in the groin area include swelling and tenderness, difficulty standing or walking, and a visible bulge. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Inguinal hernias
An inguinal hernia is a common medical condition whereby a part of the intestine or other abdominal contents protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias are most common in men, as they are more likely to have a weak spot in the abdominal wall due to a congenital birth defect.
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia include a bulge in the groin area, pain or discomfort in the groin area, and a feeling of heaviness or pressure. In some cases, the hernia can become strangulated, meaning the blood supply to the tissue is cut off, leading to severe pain and infection.
Treatment for an inguinal hernia typically involves surgery to repair the weakened abdominal wall, although some hernias can be managed with medication and lifestyle modifications.
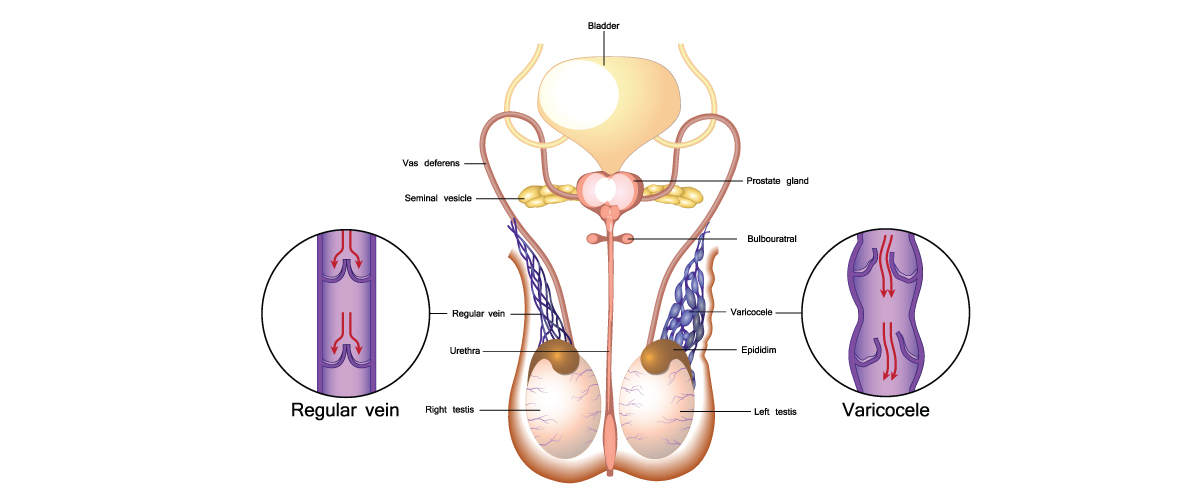
4. Varicocele
Varicocele is a condition in which the veins in the scrotum become dilated and twisted, leading to the pooling of blood in the veins surrounding the testicles. This can cause a range of symptoms, including testicular pain.
The pain from varicocele is often described as a dull, aching sensation radiating through to the lower abdomen or groin area. It can feel worse after standing or physical activity, and worsened by heat or tight clothing. Other symptoms of varicocele include swelling, heaviness, and a feeling of fullness. In some cases, varicocele can cause testicular atrophy, shrinkage, and infertility.
5. Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is a medical condition in which the spermatic cord, which supplies blood to the testicles, becomes twisted. When the spermatic cord becomes twisted, it can decrease blood flow to the testicles and cause a lack of oxygen, along with an accumulation of waste products, leading to pain, swelling, and possibly even tissue death.
The most common cause of testicular torsion is a congenital defect in which one testicle is not attached correctly, causing it to be prone to twisting. Testicular torsion can also occur when the testicles are not adequately supported by the scrotal sac or if the testicles are too large or heavy. Other causes of testicular torsion can include trauma, strenuous physical activity, and infection or inflammation of the testicle.
The sudden, sharp pain associated with testicular torsion is often severe and requires immediate medical attention. If left untreated, testicular torsion can lead to reduced blood flow to the testicles and permanent damage.
6. Testicular trauma
Testicular trauma is an injury to one or both testicles that causes severe pain and discomfort. The testicles are very sensitive, and any type of trauma, whether a direct blow or a sharp object, can cause significant pain. Testicular trauma can also cause swelling, bruising, inflammation, or internal bleeding.
Testicular trauma can also be caused by a medical procedure, such as hernia surgery. This type of trauma can cause damage to the scrotum, testicles, or both, leading to pain and swelling. In some cases, the trauma can cause bleeding in the testicle or a rupture of the testicle, both of which can be dangerous and require medical attention.
7. Kidney stones
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys. Caused by various factors, including dehydration, high levels of certain minerals in the urine, and an imbalance in the body’s acid base, kidney stones range in size, from a few millimetres to several centimetres. They are one of the most common urinary tract disorders, affecting as many as 10-15% of the population and can cause considerable pain and discomfort.
The most common way for kidney stones to cause testicular pain is when a kidney stone passes through the ureter and becomes lodged in the urethra, causing a blockage. This blockage can cause pressure in the urinary tract, which then transfers to the testicles, resulting in pain. Another way is when kidney stones become lodged in the bladder or ureter. When this occurs, the pressure created by the stone can cause irritation and inflammation of the surrounding tissues, which can cause pain in the testicles. The pain is usually localised on one side, ranging from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation.

8. Sexually transmitted infection (STI)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause various symptoms, including testicular pain. Common STIs that can cause testicular pain include gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis. In men, these infections can cause inflammation in the epididymis, the tube connecting the testicles to the vas deferens. This inflammation can lead to pain and swelling of the testicles.
In some cases, an STI can cause an abscess in the testicles, leading to severe pain and discomfort. Other symptoms of STIs may also be present, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. It is important to see a doctor if you have any of these symptoms, as they may be indicative of an STI that may require treatment.
Find out 7 sexual health facts every man should know.
9. Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by bacteria that enter the urinary system, usually through the urethra. While UTIs typically affect the bladder and urethra, they can also spread to other body areas, including the testicles. When this happens, testicular pain can be the result. This pain is usually described as a dull ache or a burning sensation and can range from mild to severe. It can also accompany other symptoms, such as fever, chills, nausea, and fatigue.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are much more common in women than men. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), UTIs are responsible for up to 8.1 million doctor visits yearly, and 90% of those are among women. This is because women’s urinary tracts are shorter than men’s, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder and cause an infection. That said, men can still get UTIs, especially if they have an enlarged prostate or a weakened immune system. Men should also be aware of the risk factors for UTIs, such as not drinking enough fluids and having unprotected sex.
10. Testicular cancer
Understandably, it’s easy to jump to worst-case conclusions at the first signs of testicular pain. However, it is important to note that testicular pain is not necessarily indicative of cancer. In most cases, testicular pain is caused by a non-cancerous condition such as an infection or injury.
It is still important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing testicular pain, as testicular cancer can be treated successfully if discovered early. It is best to see a doctor as soon as possible, so early diagnosis and treatment can take place.
How common is testicular cancer in Australia?
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in young men aged between 15 and 40 in Australia. According to Cancer Council Australia, testicular cancer accounts for around 3% of all new cancer cases in men.
While the exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, it is thought to be linked to genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the disease, being born with an undescended testicle, and having abnormal testicular development.
With early detection and treatment, testicular cancer is highly treatable and often curable. Symptoms may include a lump or swelling on a testicle, a change in size or shape of a testicle, pain or discomfort in the testicles, and a buildup of fluid in the scrotum. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to discuss them with your doctor.
When to visit the doctor about testicular pain?
Testicular pain is a symptom that should never be ignored. In most cases, testicular pain is not a medical emergency; however, you should see a doctor if you experience any pain that lasts longer than a few days. You should also see a doctor if you experience other symptoms, such as swelling, redness, or discharge, in addition to testicular pain. Sometimes, the pain may be caused by an infection or other medical condition, and prompt treatment is necessary to prevent further complications.
Show up for yourself and take care of your health with Stagger.